According to the newest Future of Jobs Report 2023 by the World Economic Forum, the technology adaptation will remain a key driver of business transformation in the next five years. This year’s report brings together the perspectives of 803 companies – collectively employing more than 11.3 million workers across 27 industry clusters and 45 economies from all world regions. The report covers all labor market segments, although, in the following summary, we only focus on changes and forecasts related to technology and artificial intelligence.
Table of Contents
Key Findings
The largest job creation and destruction effects come from environmental, technological, and economic trends. Climate change adaptation is rated as a net job creator, together with technological advancement. Still, net job destruction is expected d due to slower economic growth, supply shortage, and rising costs. Over 75% of companies want to adopt big data, cloud computing, and AI features in the next five years, and expected to be a net positive impact on job creation. In the technology sector, big data analytics, encryption, and cybersecurity will be the biggest driver of job growth.
Respondents to the survey projected 83 million jobs to be lost and 69 million are projected to be created in the next five years, constitution a 23% structural labor-market churn. The report suggests a higher-than-average churn in the Supply Chain and Transportation and Media, Entertainment, and Spor s industries. A significant factor in the decrease in administrative jobs is the automation of business-related tasks performed by machines. Organizations today estimate a 34% automated task share, which can grow to 42% by 2027. Information and data processing is predicted to be the most automated tasks, with a projected automation share of 65%.
The majority of the fastest-growing roles are technology-related ones, like AI and ML Specialists, BI Analysts, and Information Security Analysts, but Renewable Energy jobs will also grow fast. The majority of the fastest declining roles are clerical or secretarial roles like Bank and Postal Clerks, Ticket and Data entry Clerks. Large-scale job growth is expected in education, agriculture, digital commerce, and trade.
Analytical and creative thinking remain the most important skills for workers in 2023. The Top most important skills will be Problem-Solving, Creative Thinking, and Technology literacy. In the coming 5 years, 60% of workers will require training, but only half of them have access to adequate training opportunities today. The priority for workforce development is to promote creative and analytical thinking, but employers also plan to focus on leadership and social influence.
Fastest-Growing Jobs
Research conducted by LinkedIn for the Future of Jobs Report 2023 describes the 100 roles that have grown fastest, consistently and globally, over the last four years – known as the “Jobs on the Rise”. Such employment reports frequently created by Lin edIn based on geological location, like Jobs on the Rise US, Europe or Southeast Asia.
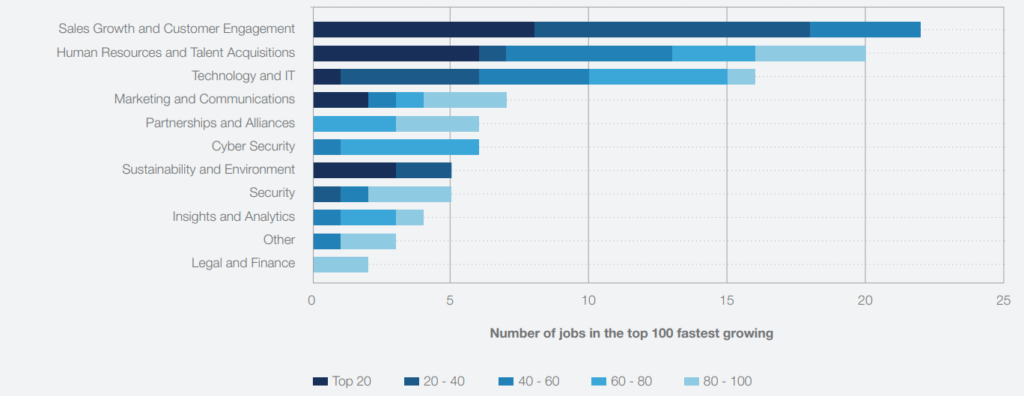
According to the report, the I formation Technology and Digital Communication sector is experiencing significant growth in job opportunities. Among the top 100 jobs on the rise, 16 are technology and IT-related roles, making it the third-highest job grouping. Sales growth and customer engagement roles take the top spot with 22 of the 100 roles, including titles such as Director of Growth and Customer Success Engineer. This suggests a growing emphasis on expanding customer groups and growth models in a world with increasing digital access and rapid technological advancement. The second most popular job grouping is Human Resources and Talent Acquisition, with a focus on talent acquisition and recruitment, including a specific role for Information Technology Recruitment.
Expected Impact of Macro Trends
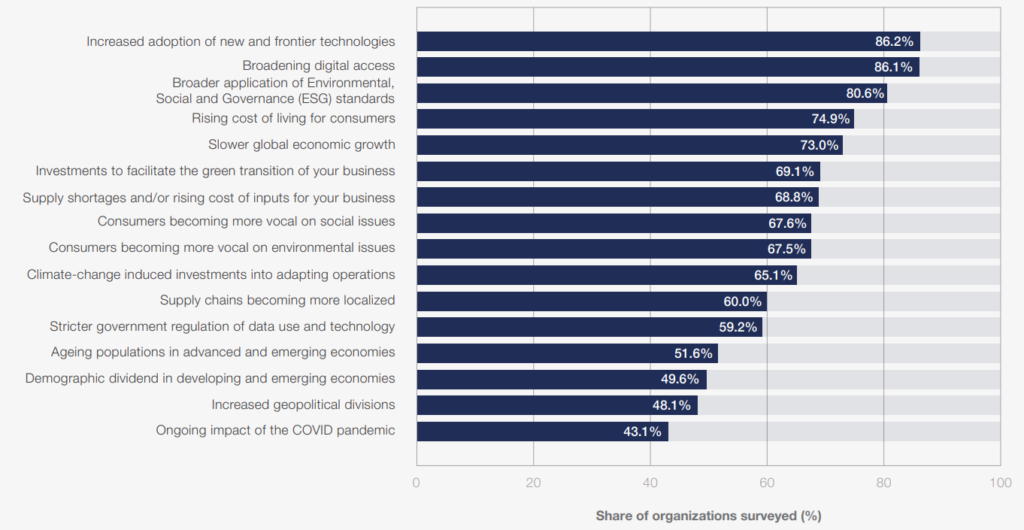
There is a section in the report we you can get market expectations about the major macro trends that will drive the business transformation in the next five years. As shown in the figure below, the Adaptation of new and frontier technologies and the broadening of digital access are most likely to impact the organizations surveyed. 85% believed that the AI and digitalization trends will have a serious impact on their development, and are expected to be a net job-creating factor. Nearly 75% of the organizations stated that the Rising cost of living and the Slower global economic growth will affect their operations, and these will also be the most serious job displacer macro trends.
Expected Impact of Technology Adaptation
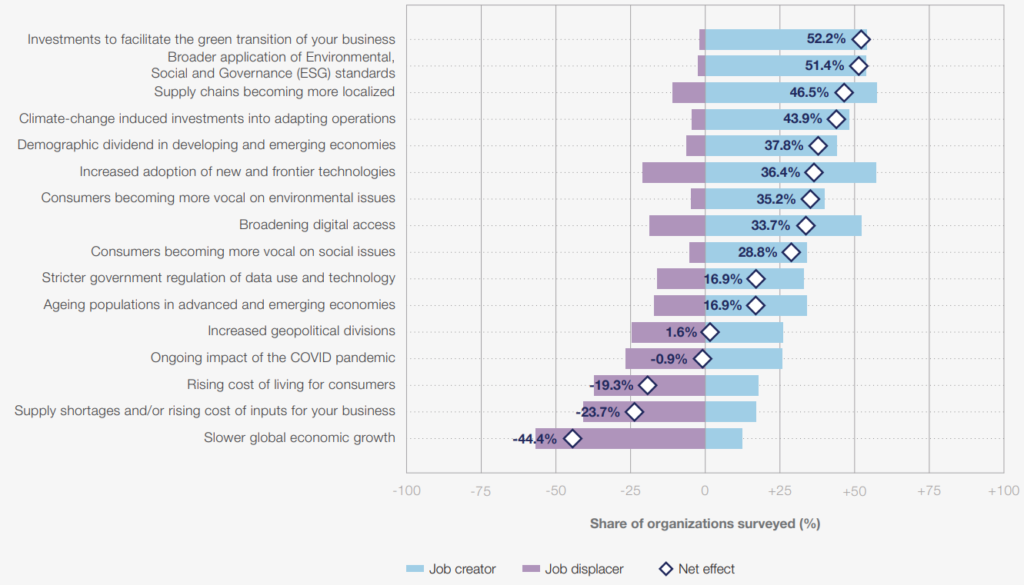
The questionnaire also looked for the answer to what effect each technology se ment will have on operations development in the next 5 years. Based on the analysis, it was found that, out of the 28 IT activities examined, in almost all cases (except for 2), will impact the labor market as a net job creator. Big Data Analytics, Climate Change. Environmental Management Technologies, and Encryption, and Cybersecurity are expected to be the biggest drivers of job growth. Only Robotics (humanoid and non-humanoid), are estimated to have net job displacer, but only with an average of 5%. Artificial Intelligence forecasted a significant labor market disruption, where many companies will create many new jobs with their huge growth, but there will be those who will be less fortunate, and their role will decrease. All in all, the AI subsector is expected to be a ~ 25% net job creator.
When we focus on the field of robotics and analyze the data provided by the International Federation of Robotics, it becomes apparent that the density of industrial robots per 10,000 workers has been on a steady rise for the past five years. In fact, the density has almost doubled in this time period, with an average of 126 robots per 10,000 workers.
The Human-Machine Frontier
Due to the last 5 years’ trend (boosted by the COVID-19 lockdowns), the business adaptation of frontier technologies increased a lot, and now we can see now significant shift between the data processing tasks performed by humans and those performed by algorithms. According to current estimates, machines are responsible for approximately 34% of business-related tasks, while the remaining 66% are performed by humans. It is predicted that by 2027, automation levels will range from 35% for reasoning and decision-making tasks to 65% for information and data processing tasks.
It is expected that the use of A technology will continue to grow in various industries over the next few years. It is uncertain how rapidly developing technologies, like generative AI, will affect the types of tasks that can be automated between 2023 and 2027. However, based on recent studies that the combination of Large Language Models such as ChatGPT and applications that address known issues, like factual inaccuracies, can increase the share of data automation by up to 50%.

Labor Market Churn
Overall the Future of Jobs Report estimates an average structural labor market churn of 23% for the surveyed companies across sectors and countries over the next five years. This includes both new roles being created and existing ones being destroyed in this time period, which will represent 23% of the current workforce.
Related to different sectors, the churn analysis forecasts a higher than average churn from 2023 to 2027 in the Supply Chain, Transportation, Media and Entertainment, and the Sports sector. Lower than average churn is Accommodation, Food and Leisure; Manufacturing and Retail and Wholesale of Customer Goods.
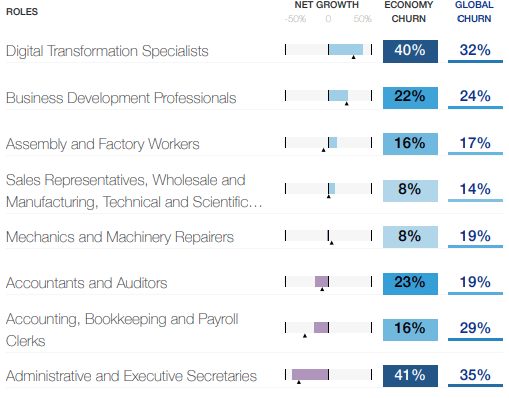
AI and Machine Learning Specialists top the list of fast-growing jobs, followed by Sustainability Specialist and Business Intelligence Analysts. The majority of the fastest declining roles are clerical or secretarial roles like Data Entry Clerks, Executive Secretaries, A counting, and Bookkeeping.
Disruptions to Skills
In this report, the surveyed companies predict that 44% of workers’ skills would be disrupted in the following five years. In the previous period the COVID-19 was the main driver of this disruption, but in the upcoming period, surely the technology adaptations and the environmental change will be the main cause.
Core Skills in 2023
Many companies prioritize Analytical Thinking as a core skill, making up a 9% share of average skill sets. Creative Thinking follows closely in second place, surpassing three self-efficacy skills: resilience, flexibility, and agility; motivation and self-awareness; and curiosity and lifelong learning. Comparisons to past surveys indicate that Creative Thinking is becoming increasingly important relative to Analytical Thinking, as more workplace tasks become automated. The gap between the two has significantly decreased and may continue to narrow.

Skill Evolution 2023-2027
According to recent reports, cognitive skills are becoming increasingly important in the workplace due to the growing need for complex problem-solving. In terms of socio-emotional attitudes, businesses are placing a high value on curiosity and lifelong learning, resilience, flexibility, agility, motivation, and self-awareness. Although no specific skills are in decline, writing and mathematics, manual dexterity, endurance, and precision are considered less important by surveyed organizations.
Technology skills, which comprise AI and big data, Networks and Cybersecurity, Technological literacy, Design and user experience, and Programming skills, are growing in demand most quickly in the Care, Personal services and Well-being; Insurance and Pensions Management; and Financial Services sectors.
Reskilling and Upskilling
The highest priority for skills training in the upcoming 5 years is analytical thinking, which is set to account for 10% of training initiatives, on average. The second priority for workforce development is to promote creative thinking.
Although companies recognize the importance of various cognitive skills, their corporate upskilling strategies do not always reflect the skills that are increasing in significance the fastest. Interestingly, companies seem to prioritize AI and big data, as well as leadership and social influence, much more highly than their current importance to their workforce. In fact, surveyed companies rank AI and big data 12 places higher in their skills strategies compared to their evaluation of core skills, and plan to invest an estimated 9% of their reskilling efforts in these areas.
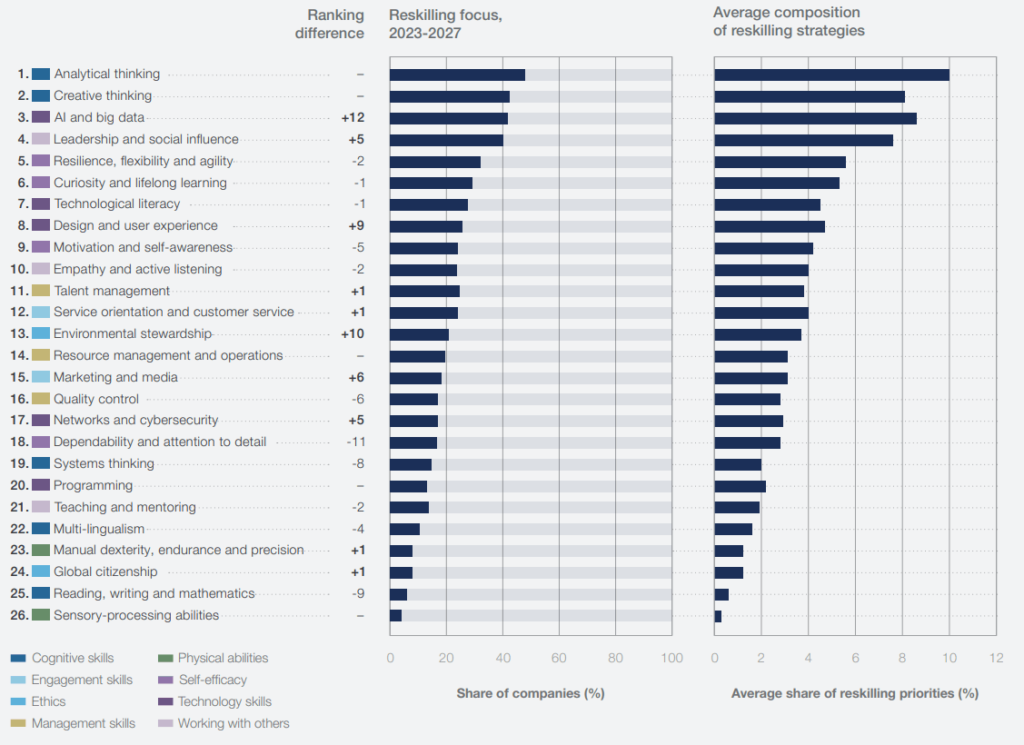
AI and Big Data
Although AI and big data are currently only ranked 15th as a core skills for mass employment, they have become the third most important priority in company training strategies for the next five years. For companies with more than 50,000 employees, AI and big data are the Top priority in workforce reskilling strategy. When it comes to technology skills, the ability to efficiently use AI tools has surpassed human computer programming, network and cyber security skills, as well as design and user experience.
According to recent studies, big data analytics ranks third among the technologies that companies are likely to adopt by 2027. As per the findings, 80% of companies are planning to incorporate it more extensively into their operations, while 75% of them intend to include AI techniques like machine learning and neural networks.
Conclusion
While in early 2023, pessimistic predictions regarding the jobs impact of the green transition and generative AI dominate the media headlines, these areas have also been identified as some of the largest drivers of future job creation by the surveyed companies. While skills disruption remains high, it has somewhat stabilized from the tight of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“It’s very clear that there is a hollowing out happening off the labor market based on skill levels. In the last few years, it’s really been about the concern around industrial robots displacing those that work in factories, for example. Now to some extent, there has been that displacement, but to some extent, there’s also been a lot of growth in terms of the advanced manufacturing workforce. A very similar pattern is now emerging when it comes to artificial intelligence. Those that are at the lower end of the skills, around administrative and secretarial work, now risk being disrupted by AI, especially generative AI, and at the same time, there is a lot of growth in higher value-add roles. We are seeing a very similar inflection point now, and there are some of that risks, but the net result is still positive when it comes to technology impacting jobs.” Saadia Zahidi – Managing Director of the World Economic Forum
While generative AI has the potential to displace jobs, the emphasis on training workforces to take advantage of AI and big data highlights the potential for new roles that can harness its capabilities to help achieve business goals.








































